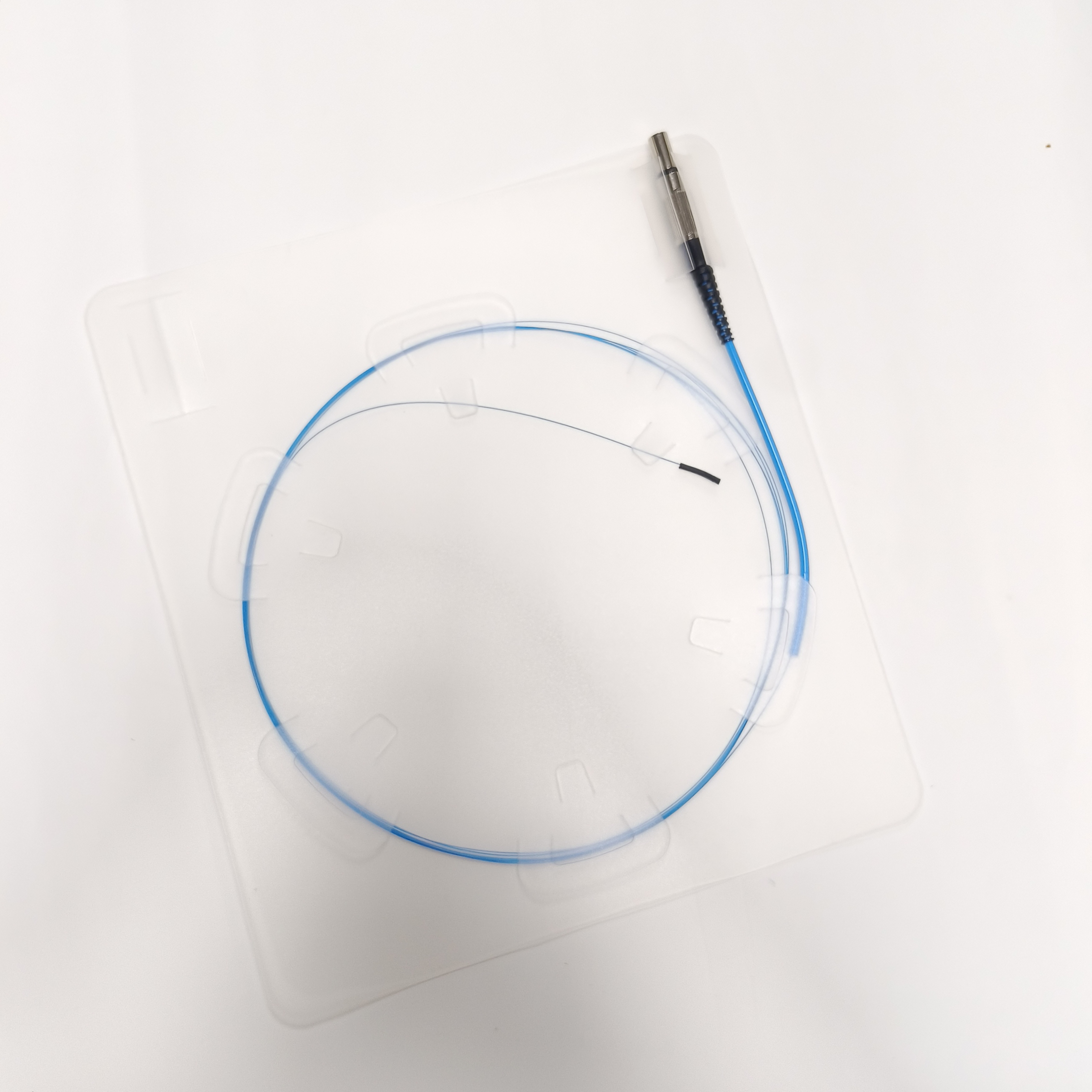
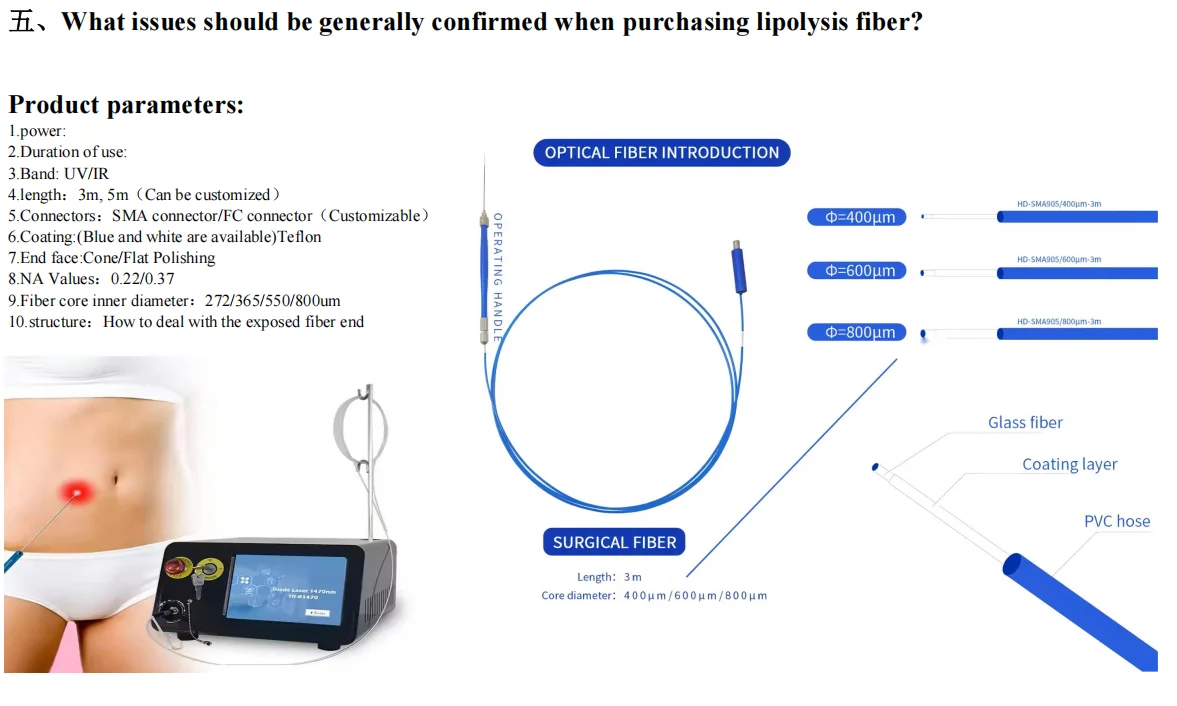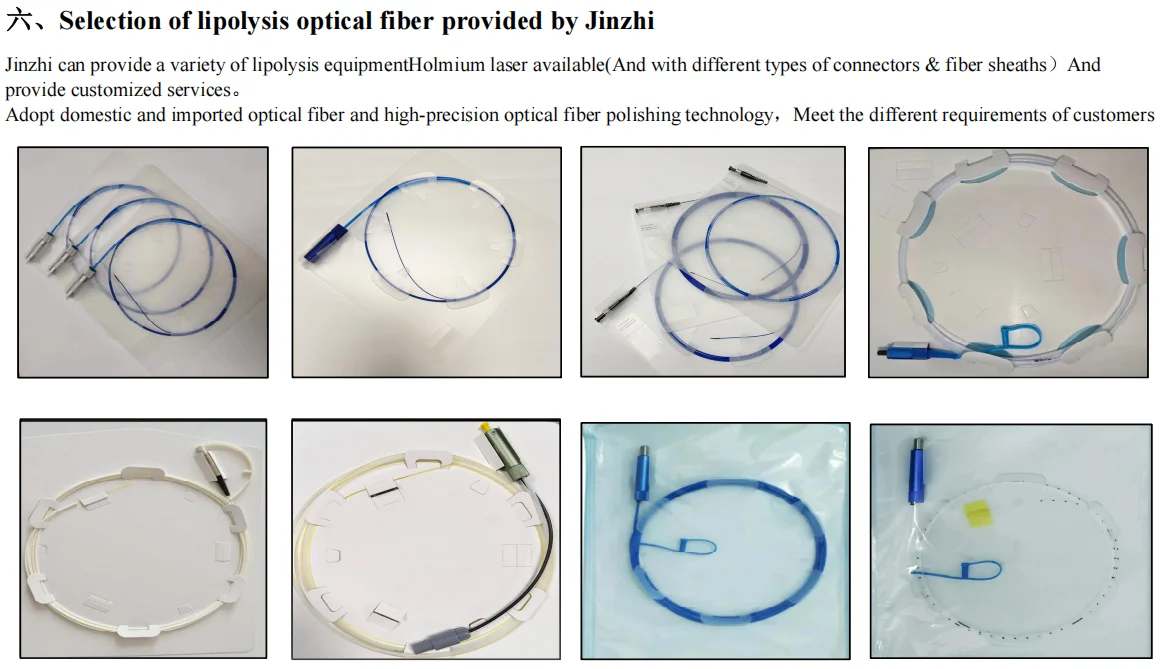






The lipolytic fiber transmits laser energy of a specific wavelength into the subcutaneous fat layer through a thin fiber optic cable. After the laser energy is absorbed by adipocytes, it is converted into thermal energy, causing the adipocyte membrane to rupture and release components such as fatty acids, glycerol, and water.
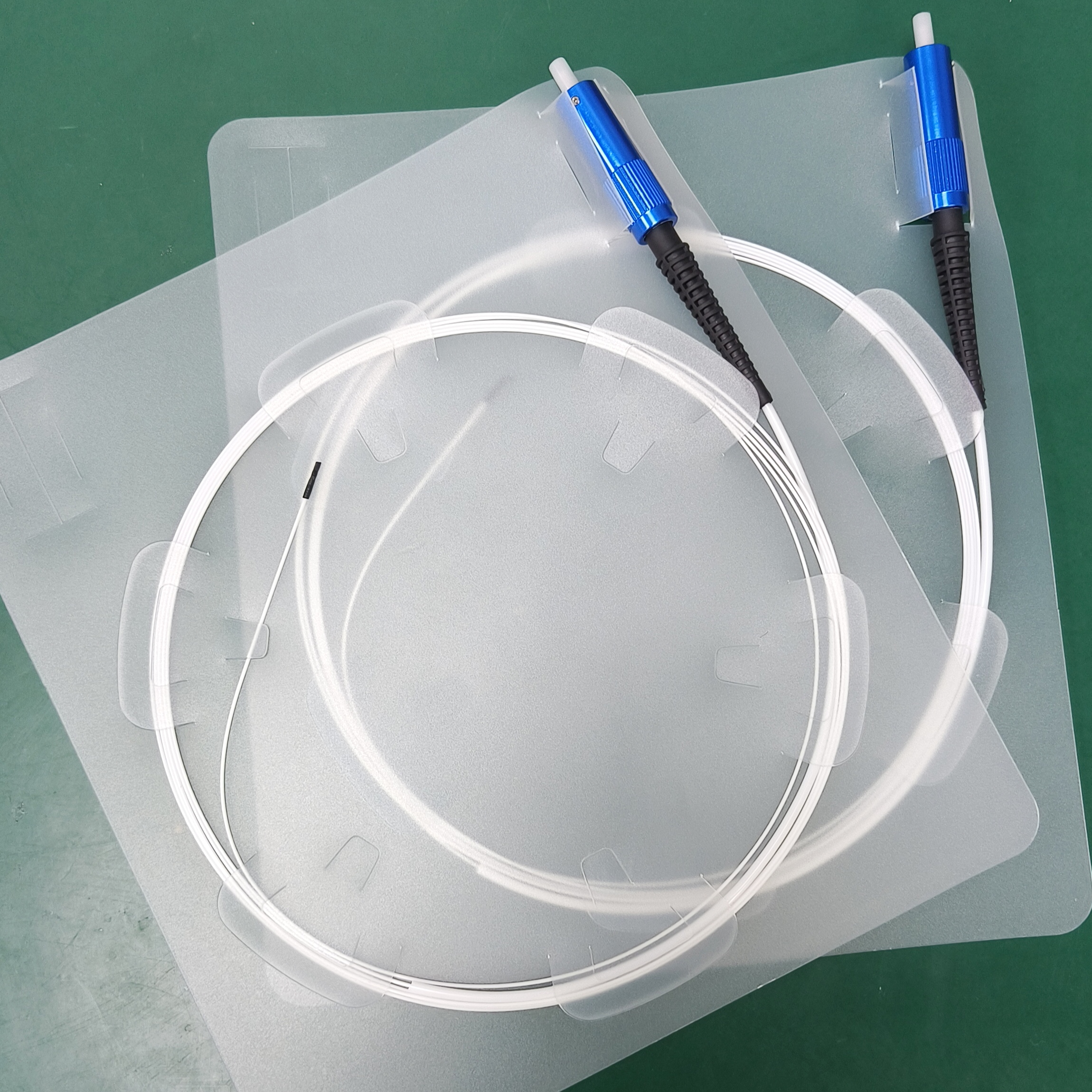
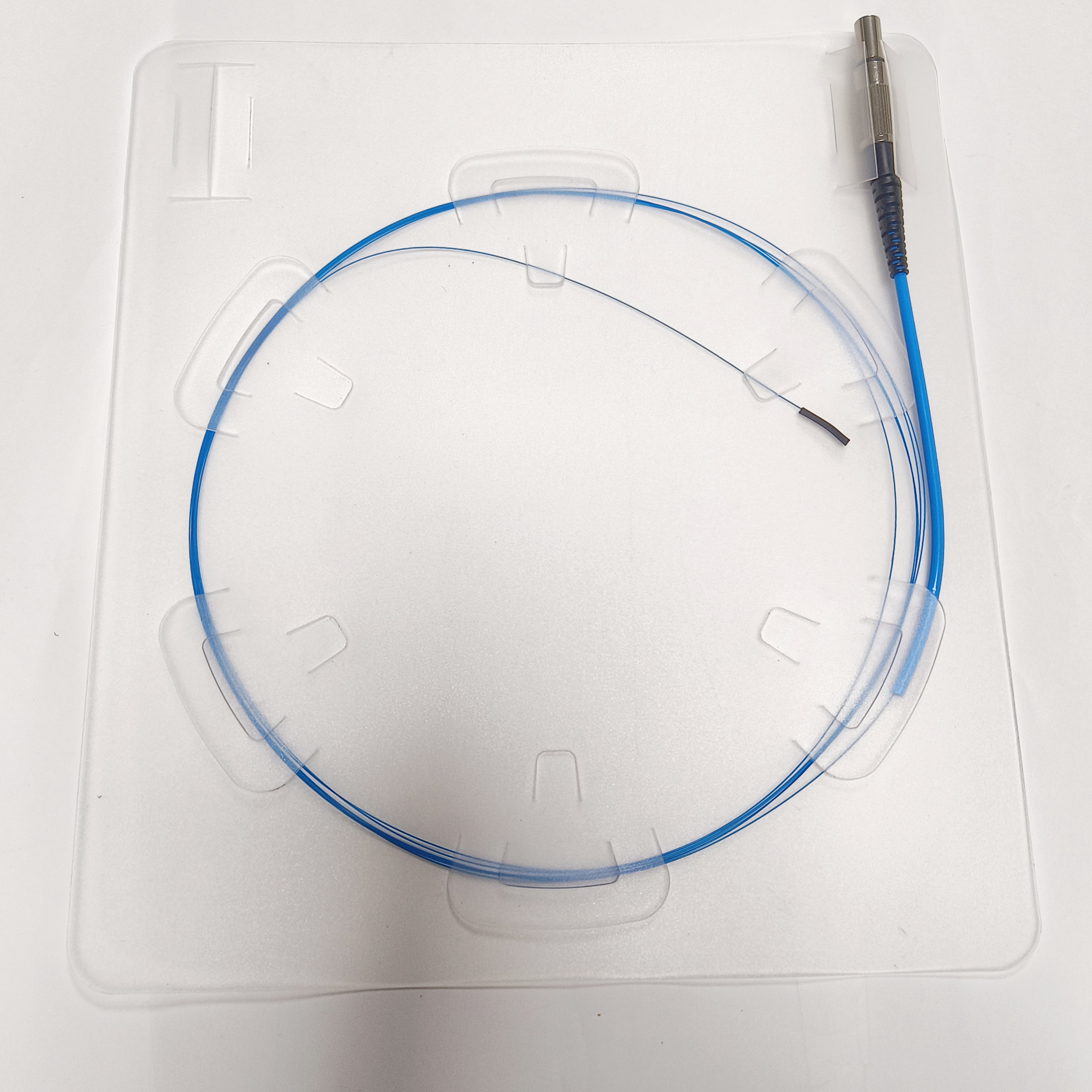
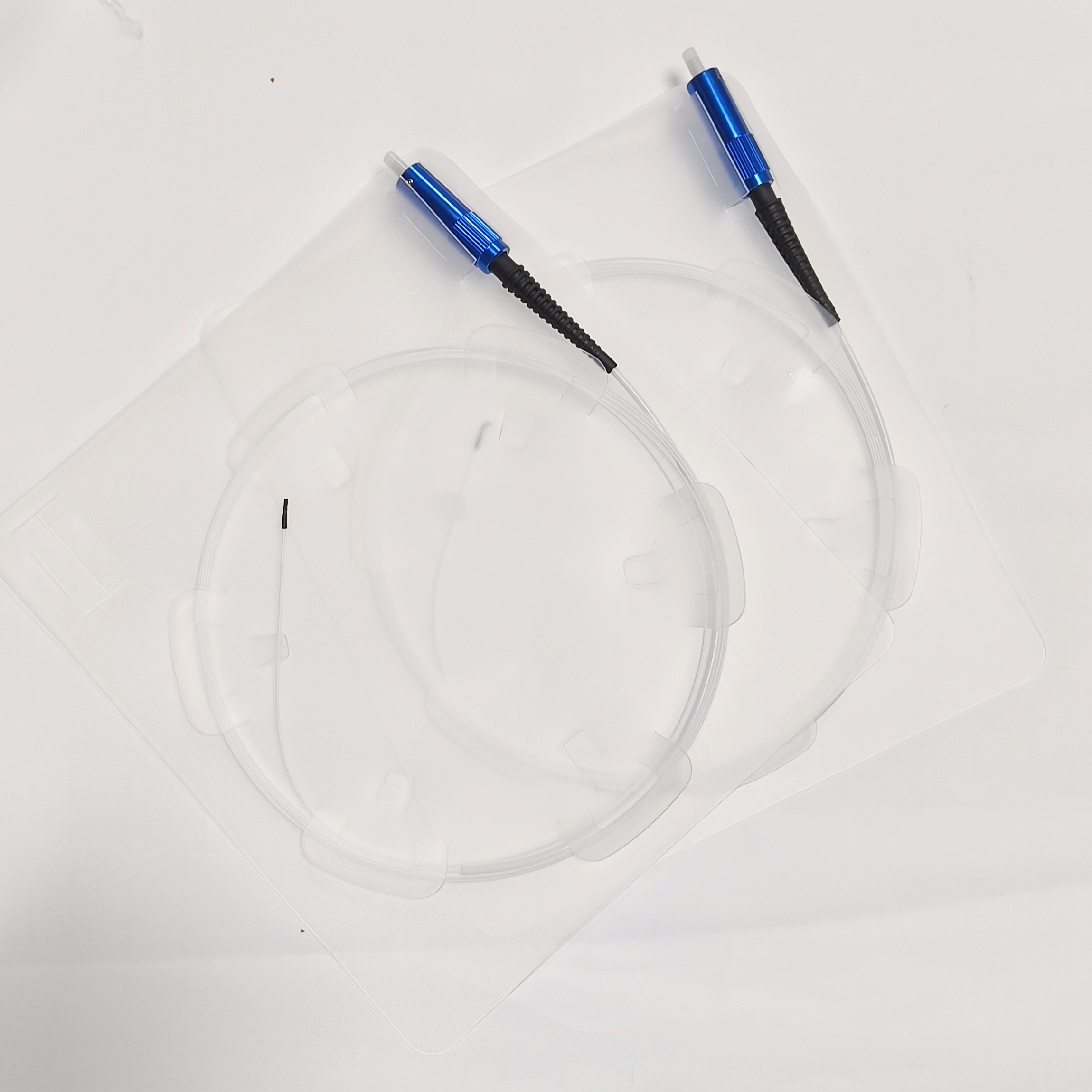
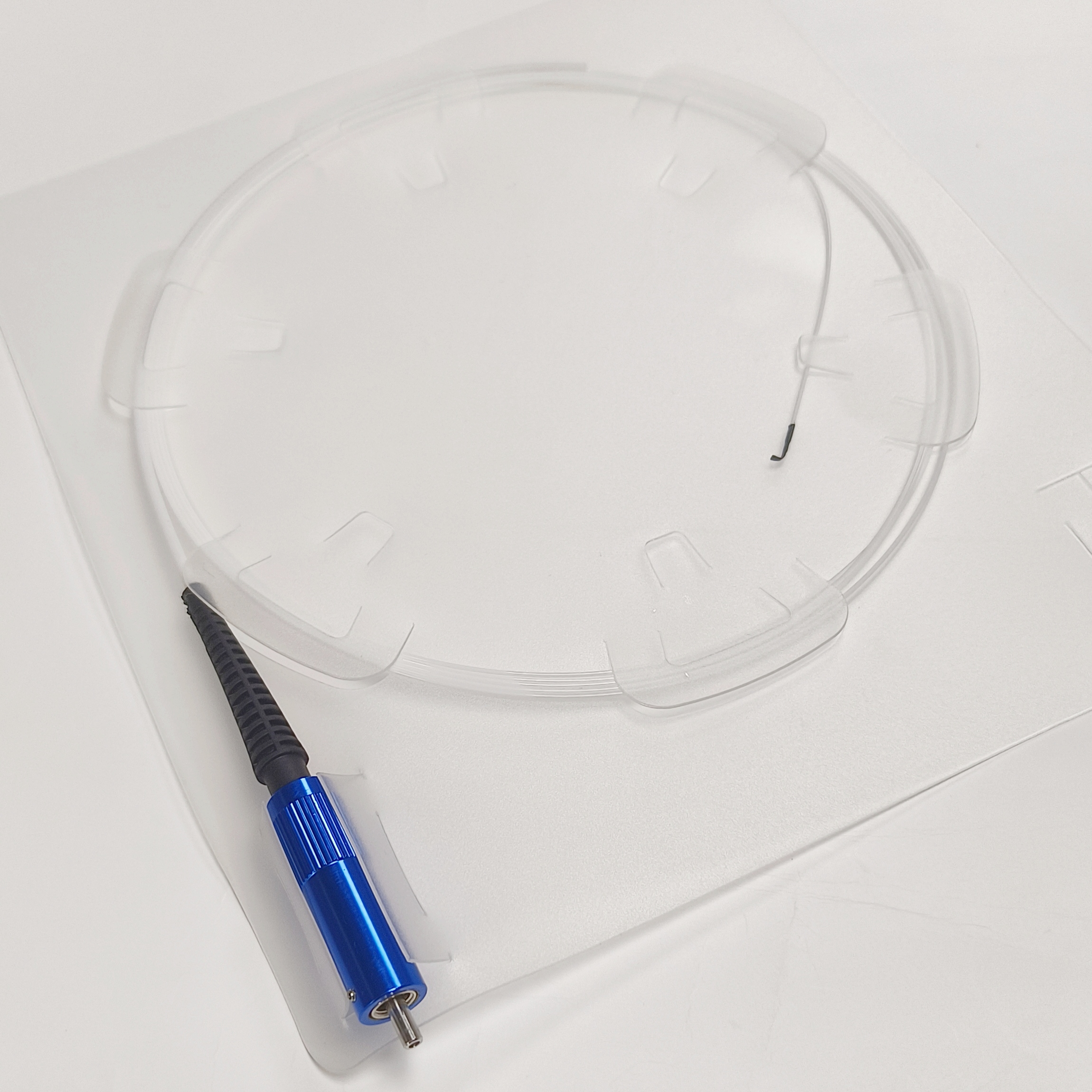
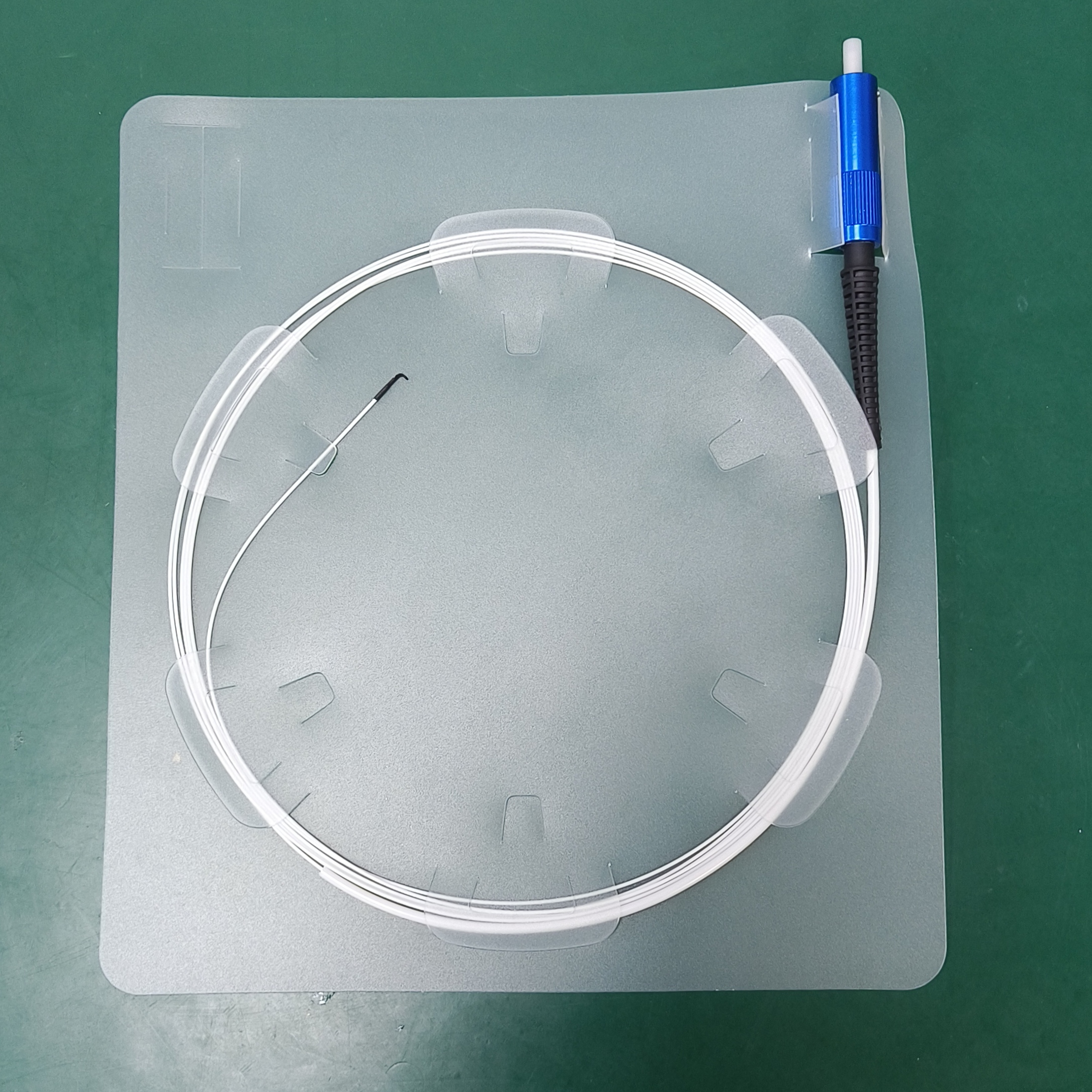
Polyimide Optical Fiber for Lipid Dissolution
Structure
Fiber core: made of high-purity SiO₂ and doped with a very small amount of dopants.
Cladding: made of high-purity SiO₂ and contains a very small amount of dopants, due to which the refractive index of the cladding is slightly lower than the refractive index of the fiber core.
Coating: protects the optical fiber from erosion by water vapor and mechanical abrasion, while increasing the mechanical strength and flexibility of the optical fiber, which helps to extend its service life.
Connector: one end of the polymer-insulated optical cable is usually equipped with a special SMA905 connector, which is used to connect the optical cable to laser equipment.