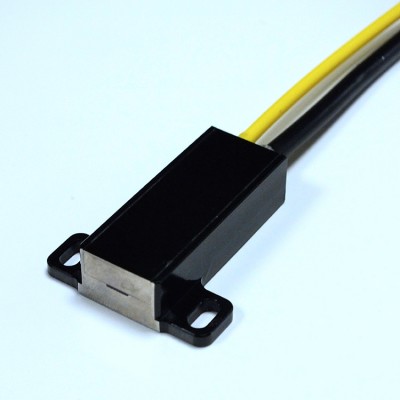



The spectrometer one-to-two fiber optic cable is a special fiber optic cable used in spectrometer systems. It is also called a two-way fiber because of its Y-shaped shape. It can convert one optical path into two optical paths and is often used in scenarios where spectral information from different light sources or different positions needs to be collected simultaneously.
Structural features
1. Fiber structure: It usually contains two optical fibers with parallel core diameters, which are composed of a core, a cladding and a coating. The core is generally made of pure quartz material with a high refractive index for transmitting optical signals; the cladding is a quartz material doped with a low refractive index, which can limit the light to be transmitted in the core.
2. Optical properties:
Spectral range: The spectral range is wide and can be selected according to needs. Common ones include ultraviolet-visible light range, visible light-near infrared range, etc., and mixed wavelengths can also be used to meet the requirements of different spectrometers and measurement scenarios.
3. Transmission loss: The transmission loss of optical fiber cable is low, which can ensure that the optical signal maintains a high intensity during transmission to ensure that the spectrometer can receive enough optical signals for accurate measurement.
Typical application scenarios
1.Dual-channel spectral detection: The same light source is split to two spectrometers for comparative analysis or redundant backup.
2.Process monitoring: One signal is used for real-time monitoring, and the other is used for main system feedback.
3.Laser power distribution: Split the laser to two processing heads.
Teaching experiment: Realize multi-channel output of a single light source in optical demonstration.