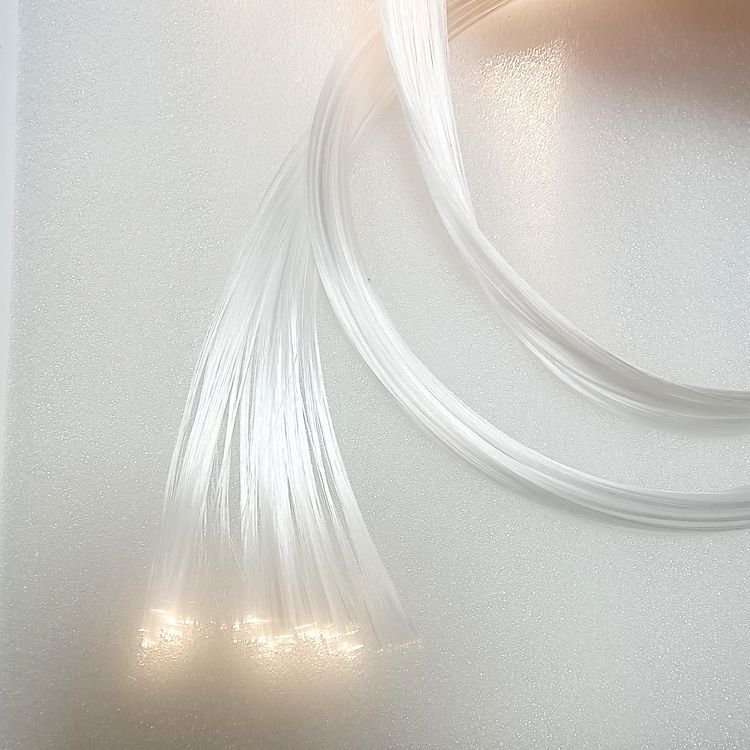
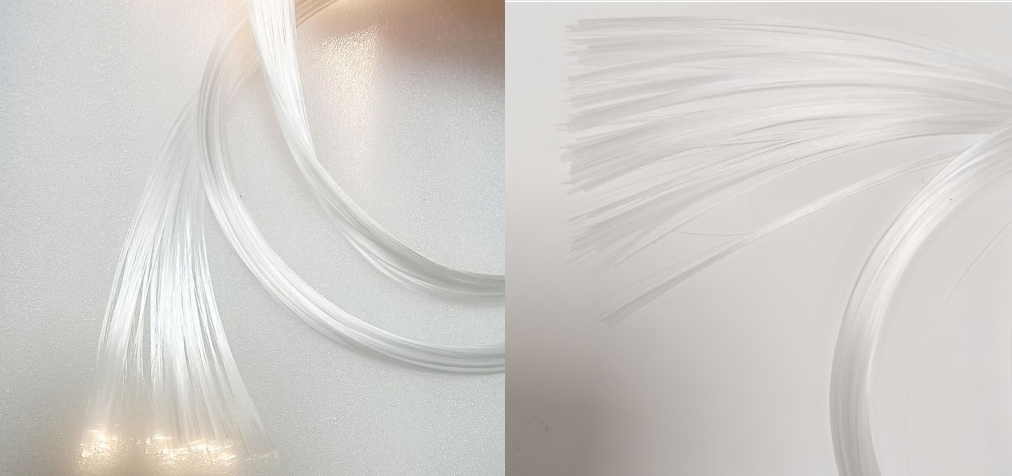


Glass fiber optic fiber usually refers to quartz glass fiber, mainly composed of silicon dioxide, which has the characteristics of being thin, transparent, and flexible, and can guide light to propagate along it. The core and cladding form a total reflection mechanism through the difference in refractive index, which ensures the efficient transmission of optical signals and can support long-distance and large-capacity information transmission.
The main features are as follows
1. Excellent optical performance:
With high-purity quartz glass as the core material, it has extremely high light transmittance, can efficiently transmit optical signals in a wide wavelength range, and has extremely low light attenuation, ensuring the stability and integrity of signals during long-distance transmission.
2. Powerful information transmission capability:
With extremely large bandwidth, a single optical fiber can achieve a transmission rate of tens of terabits per second through wavelength division multiplexing technology, far exceeding metal wires, and is the core carrier of modern large-capacity communication networks.
3. Strong physical and chemical stability:
It is chemically inert, acid- and alkali-resistant, resistant to oxidation, and has strong adaptability to humid, high-temperature and other environments; it has certain flexibility and tensile strength, can adapt to bending, wiring and other scenarios, and has a long service life.
APPLICATION
1.In the field of communication, it is the backbone transmission medium for modern long-distance communication networks, metropolitan area networks, and access networks.
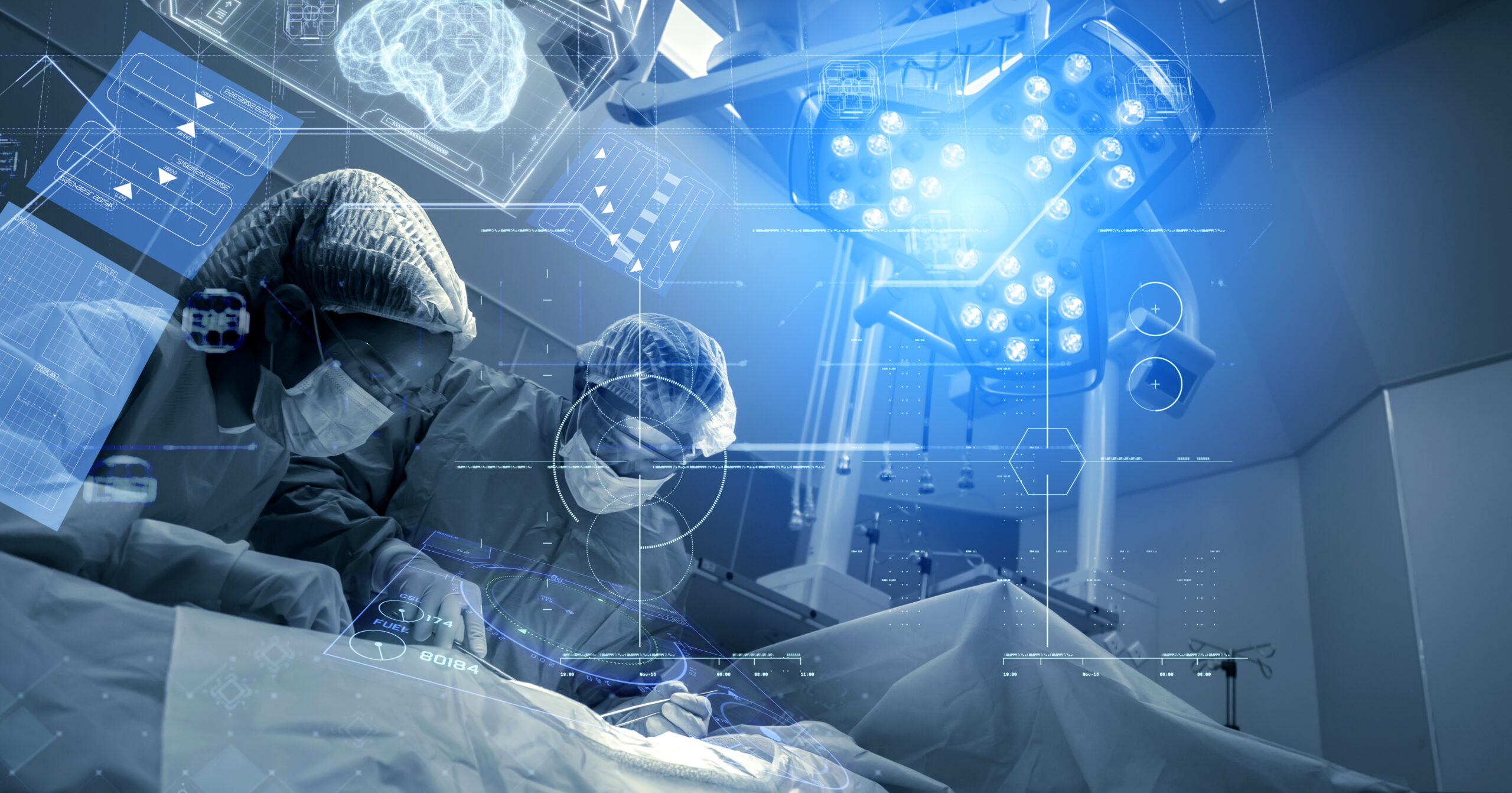
2.In the medical field, it is used to transmit light and image information in endoscopic examination equipment such as gastroscopy and colonoscopy; Used for transmitting high-energy laser beams in laser surgery.
3.In the industrial field, it can be made into fiber optic temperature sensors, fiber optic pressure sensors, etc., used to monitor the temperature, pressure and other parameters of industrial equipment
4Lighting field: used to produce fiber optic lighting fixtures, such as museum cultural relic display lighting, underwater landscape lighting, architectural contour lighting, etc
5.Military field: used to build secure, high-speed, and anti-interference communication links in military communication networks, transmitting intelligence data, combat instructions, and other information.
