

The Holmium laser is a pulsed solid-state laser that uses a Cr:Tm:Ho:YAG crystal as its active medium. It combines chromium (Cr) as the sensitizer, thulium (Tm) as the energy transfer ion, and holmium (Ho) as the active ion to generate precise and high-energy laser pulses. This technology is widely applied in urology, ENT, dermatology, and gynecology for non-invasive or minimally invasive surgical procedures, offering high accuracy and minimal patient discomfort.
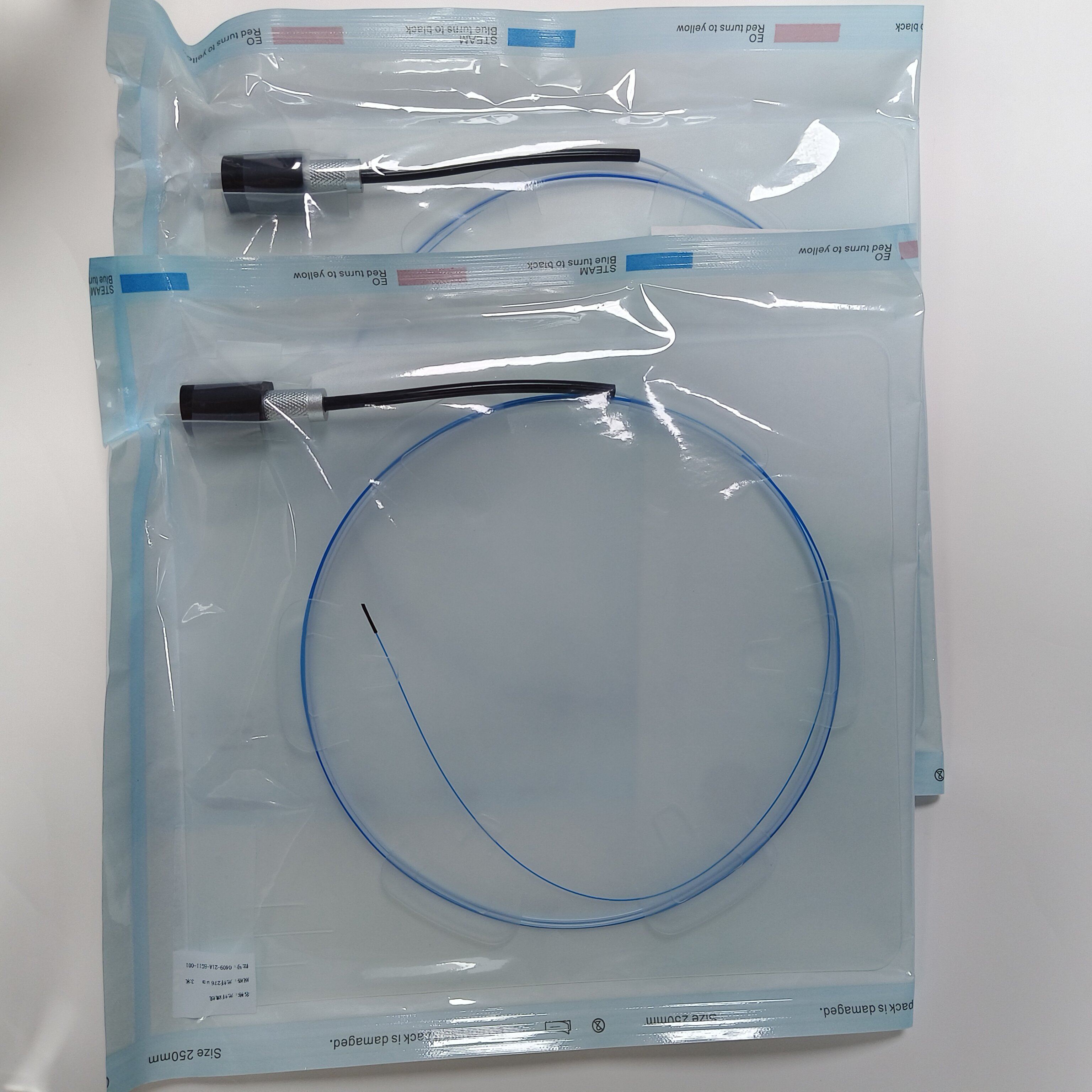
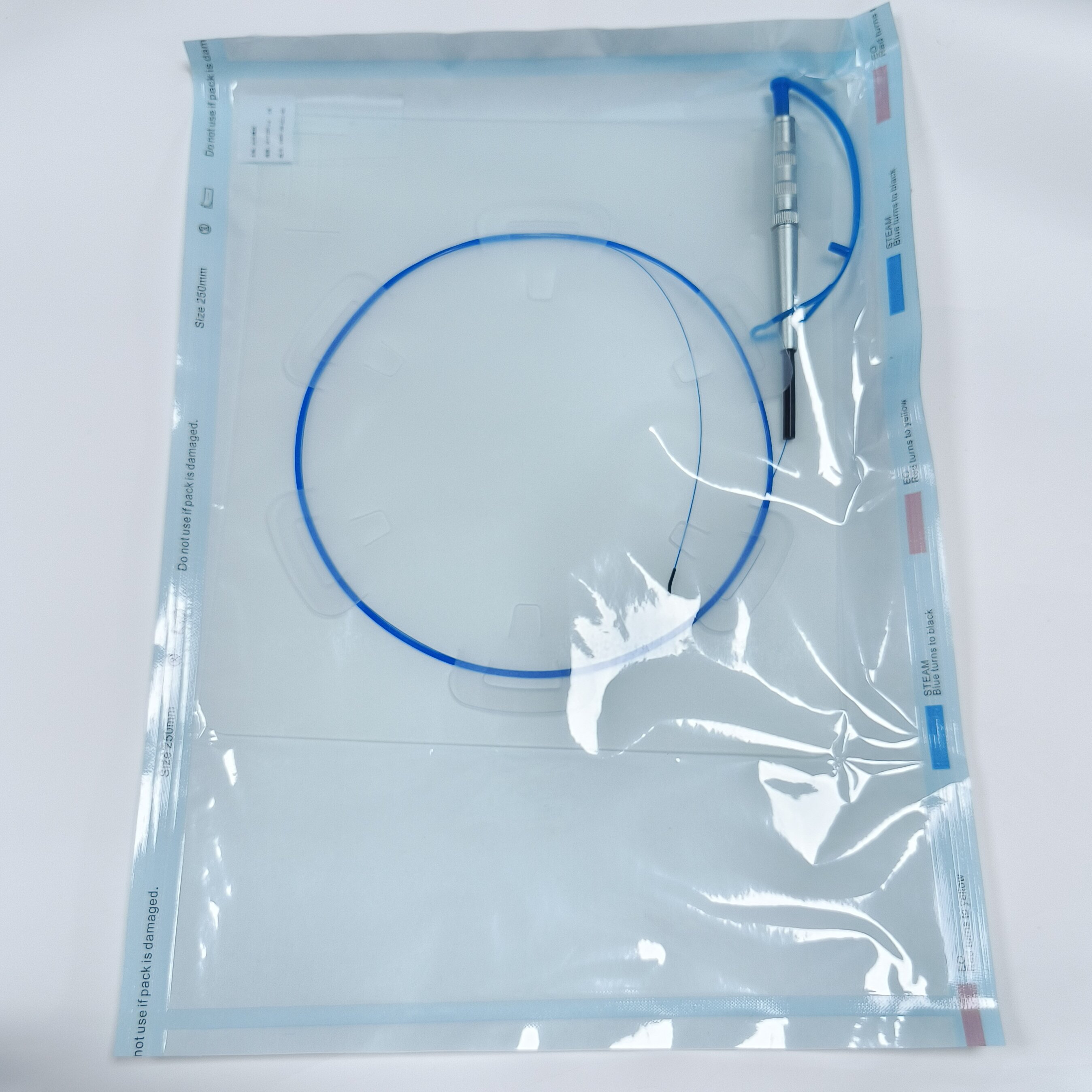
The medical holmium laser fiber is a precision light-transmission component designed for Ho:YAG (Holmium:Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser systems. It is primarily used for tissue cutting, vaporization, coagulation, and lithotripsy in minimally invasive surgical procedures across urology, ENT, and gynecology. Its key function is to deliver laser energy accurately to the target tissue while ensuring operational safety and clinical effectiveness.
Selection Considerations
When choosing a medical holmium laser fiber, the power tolerance, flexibility, and distal-end design should match the surgical application—such as stone fragmentation or soft-tissue incision—to achieve optimal efficiency.
Structure & Materials
Core: Made of low-hydroxyl quartz (SiO₂) or fluoride glass (ZBLAN) to minimize absorption loss at the 2.1 µm wavelength; available in diameters from 200 µm to 1000 µm (365 µm and 550 µm are common for lithotripsy).
Cladding: Fluorine-doped quartz with a lower refractive index than the core to maintain total internal reflection.
Coating: Metal layer (copper or stainless steel) for enhanced mechanical strength and burn protection.
Sheath: Polyimide or PTFE polymer for flexibility and biocompatibility.
Tip Design: Bare tip for direct tissue contact or ball tip for diffuse light emission, reducing the risk of perforation.
Cooling System: Optional integrated liquid-cooling channels to prevent overheating during prolonged use.
Key Features & Clinical Advantages
High-Efficiency Lithotripsy
Photothermal effect: The 2100 nm wavelength is absorbed by water in the calculus, creating an instant high temperature that fragments the stone.
Photomechanical effect: Pulsed laser energy forms cavitation bubbles and shock waves, further disintegrating hard stones.
Precision in Minimally Invasive Surgery
Compatible with ureteroscopes or nephroscopes to access stones through natural cavities or small incisions.
Enables fine control of laser energy, minimizing mucosal injury to surrounding tissues.
Simultaneous Hemostasis and Vaporization
Coagulates blood vessels and tissue to reduce intraoperative bleeding.
Efficiently vaporizes soft tissue—allowing one device to perform multiple functions.
